Sight is perhaps the most crucial sense, and the functionality of our eyes has given great insight into the study of light. The evolution of the human eye, and our understanding of light refraction, has allowed for the creation of light measurement sensors and tools in multiple fields. Read on to better understand photometry, what it is and how it is used.
Photometry Versus Radiometry
Photometry refers to the science of light measurement in terms of the light’s brightness that the human eye can perceive. Photometry, while similar to radiometry, differs greatly. Radiometry is the science that measures radiant energy and includes waves across the light spectrum. Radiometry and photometry differ in that the latter only focuses on the spectrum of light that the human eye can perceive. The two sciences are often confused, but many hold to the idea that photometry only includes the light spectrum observable through the human eye.
Principles Behind Photometers
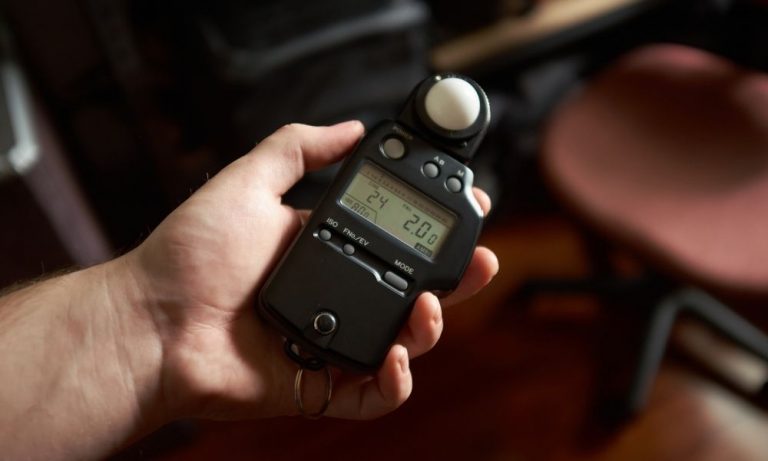
As a basic principle, photometers examine how light interacts with reflective materials. The array of photometers allow for photometry to apply in different fields of study. Some instruments are used to observe how light absorbs and/or reflects wavelengths. Other instruments measure light by converting light into an electrical current and then measuring the electrical current produced by the light. Other photometers shoot white light at surfaces to measure the amount of light that reflects back at the instrument.
Uses of Photometry and Photometers
Photometry is often used in the study of liquids and solutions in chemistry. Photometers can help measure masses of organic or inorganic materials in a solution or liquid. In astronomy, photometry is utilized by applying filters to restrict certain wavelengths and allowing other desired wavelengths through to measure. Photometers play an important role in allowing scientists to observe and capture images of celestial bodies.
Photometry and Gamma Scientific
For over 50 years, Gamma Scientific has delivered highly unique, state-of-the-art measurement solutions for manufacturers and users of light sources, sensors, and displays. The company also operates an ISO 17025, NVLAP accredited (NVLAP lab code 200823-0) laboratory for calibration and testing headquartered in San Diego, California. In addition to assuring measurement accuracy, accreditation ensures traceability to known standards, provides international acceptance of measured values, and is important for compliance purposes for your own ISO/IEC certifications.