Whether we’re taking pictures and posting them on the web or having medical imaging done, we’re engaging with a lesser-known technology called image sensors. These sensors play a significant role in creating pretty much every incredible photo you’ve ever seen or taken. And the process behind how they’re able to do this is pretty incredible, too. Take a moment to explore how image sensors work and how they’re used in our everyday lives.
What Are Image Sensors?
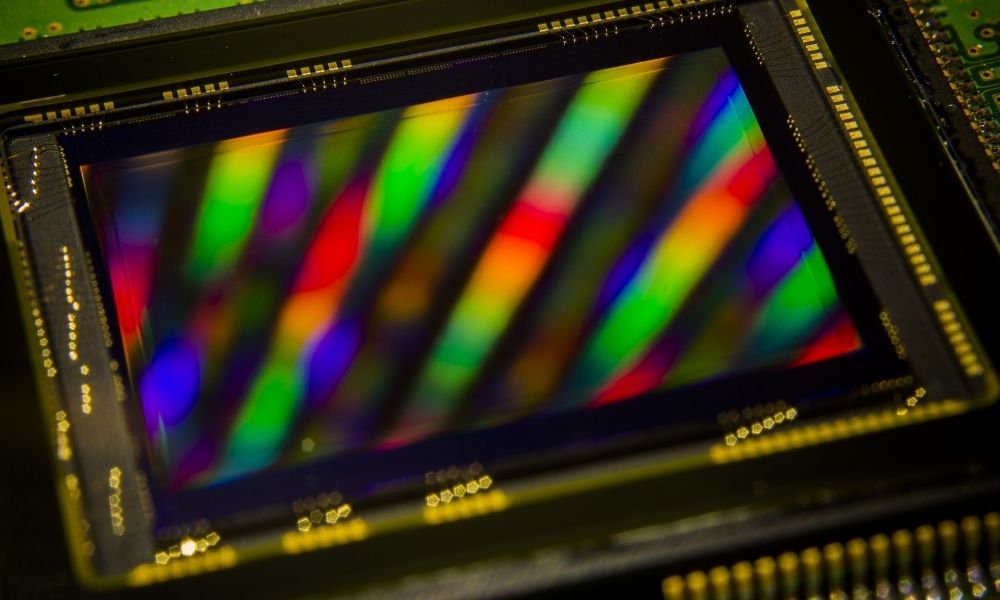
The first part of exploring what image sensors are and how we use them is all in the name. In other words, reviewing these sensors at their base level is incredibly important to our understanding of their purpose and, subsequently, their applications. In essence, image sensors are a form of technology that enables cameras to convert photons.
You could also say image sensors send light through a camera, converting it into electric signals that the camera will then process and interpret. Once the light is fully processed through the camera, it’s pushed onto internal devices capable of storing any resulting images. If this sounds at all familiar, it’s likely because image sensors are what allow us to take crystal-clear, full-color photos using any number of our personal devices.
How Do They Work?
But there’s more to what image sensors are and how we use them than basic definitions can provide. In fact, the complete transformation of light into images includes a slightly more complex internal procedure that image sensors must go through to fulfill their duties and provide accurate results.
Light has to hit certain parts of the image sensor called photodiodes. Only then can the light be converted into electric signals and pushed through to devices that piece together the image those signals create. For reference, these internal devices typically include:
- A serial shift register
- A capacitor
- An amplifier
Once the signals pass through these devices, an analog-to-digital transformation occurs. As a result, all converted electric signals are translated into binary values that can then be transformed, processed, and stored. And basically, that’s how we’re able to capture high-resolution images of all our favorite things.
How Do We Use Them?
Image sensors come in different shapes and sizes, each unique in purpose and capabilities. Because they can vary in size so much, they’re often what make devices like digital cameras, smartphones, tablets, and laptops so adept at taking excellent photos for us to put out into the ether.
On top of that, they’ve forged new and exciting paths in the photography and filming realms. But it would be incorrect to say that these are the only purposes this incredible technology serves. They’ve also presented some interesting possibilities in medical imaging solutions.
And with the image sensor characterization, imaging entities of every sector can feel confident that their imaging technology is functional and highly accurate. The point is this fantastic technology is becoming more advanced, precise, and invaluable every day. So while it already has some pretty excellent applications, there’s still a lot of space for more in the future.